
Nature’s blowtorch is an enzyme system that oxidizes toxins, drug molecules, and other noxious molecules found in the body ready for excretion. But, understanding exactly how this molecular machinery has been an ongoing research job for many years. Now, Ayyalusamy Ramamoorthy, Lucy Waskell, and Ulrich Dürr, at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, have turned to the powerful analytical technique of solid state NMR spectroscopy, to reveal important structural details about the enzyme without removing from its native site in the cell membrane.
The standard approach to working out a protein’s structure would be to extract it from the membrane, crystallize it, and then blast it with X-rays to get a clear picture of the position of every atom. Unfortunately, that does not show you the structure of the enzyme system while it is on the job. Instead, NMR bathes the sample in a strong magnetic field and then scans it with radio waves to see how the atoms respond. Depending on how the atoms in the enzyme are connected and to which and how many other atoms it is possible to build up a structural picture of the complete system.
Rams and his colleague have now found that nature’s blowtorch operates like an oxy-acetylene blowtorch. It is composed of two enzymes working together. The first enzyme, cytochrome P450, is the “acetylene”, which does the actual job of toxic breakdown, while the “oxy”, to stretch the metaphor, perhaps a little two far, is a second enzyme, cytochrome b5.
You can read more details in this week’s SpectroscopyNOW column from David Bradley together with news of the latest developments in using CDs and CD players as analytical tools for medical diagnostics and remote environmental testing. Team leader Ãngel Maquieira of the Polytechnic University of Valencia, in Spain, told me that the The robustness of a CD is perfect for collecting environmental samples, it can be used offsite, immersed in a mixture of water, sample and reagent for several minutes, washed, and then stored in a pretty much standard CD box for taking back to the lab. Once back on site, the CDs can be played in a standard computer CD drive modified with the addition of a planar photodiode to detect the signal from any sample on the CD.
Also in this week’s issue researchers in California have developed a simple algorithm, which they have integrated into a download Excel spreadsheet that gives wine makers better control over the phenolic content of their product. The input data for the spreadsheet come from a computer-interfaced ultraviolet spectrometer, which can detect the different kinds of phenolics and tannins in the wine at different stages of the production process. You can read more on that here.
 This issue, I also report on how detecting the differences between young and old hair using Raman spectroscopy is now possible, even if the hair is highly pigmented. You can find out more about that here.
This issue, I also report on how detecting the differences between young and old hair using Raman spectroscopy is now possible, even if the hair is highly pigmented. You can find out more about that here.
Finally, another enzyme story, this time about PKA, protein kinase A, and the power of X-ray crystallography, which I disputed somewhat in the NMR item!


 According to Toby Freedman, a university life “generally does not prepare individuals for careers in industry”. On the other hand, news this week that a freshman physics class just launched their own company, suggests he might on occasion be wrong. Nevertheless, an academic training is not entirely compatible with a move to the harsh realities of the commercial world and Freedman, who does hold a PhD, which she obtained from the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, and has written a book to help life scientists make the transition.
According to Toby Freedman, a university life “generally does not prepare individuals for careers in industry”. On the other hand, news this week that a freshman physics class just launched their own company, suggests he might on occasion be wrong. Nevertheless, an academic training is not entirely compatible with a move to the harsh realities of the commercial world and Freedman, who does hold a PhD, which she obtained from the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, and has written a book to help life scientists make the transition.
 Does eating chocolate give you a headache? What about red wine? Cheese, perhaps? Yes, well read on to find out how a space-age detector developed to look for signs of life on Mars could soon become the kitchen gadget of choice for anyone who suffers a painful reaction to their food.
Does eating chocolate give you a headache? What about red wine? Cheese, perhaps? Yes, well read on to find out how a space-age detector developed to look for signs of life on Mars could soon become the kitchen gadget of choice for anyone who suffers a painful reaction to their food.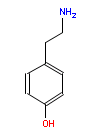 “Some foods have more biogenic amines than others,” explains Mathies, “but you cannot tell in advance because they aren’t listed on the food labels.” Even a single glass of wine has been known to trigger elevated blood pressure, heart rate and headaches in some people, he adds. He suggests that food manufactures and wine producers should be obliged to list biogenic amine content in their products by law. Although if they did, then this would preclude the need for the test kit, I assume, so the research team could concentrate on sending it to Mars instead.
“Some foods have more biogenic amines than others,” explains Mathies, “but you cannot tell in advance because they aren’t listed on the food labels.” Even a single glass of wine has been known to trigger elevated blood pressure, heart rate and headaches in some people, he adds. He suggests that food manufactures and wine producers should be obliged to list biogenic amine content in their products by law. Although if they did, then this would preclude the need for the test kit, I assume, so the research team could concentrate on sending it to Mars instead.
 This issue, I also report on how detecting the differences between young and old hair using Raman spectroscopy is now possible, even if the hair is highly pigmented. You can find out more about that here.
This issue, I also report on how detecting the differences between young and old hair using Raman spectroscopy is now possible, even if the hair is highly pigmented. You can find out more about that here.