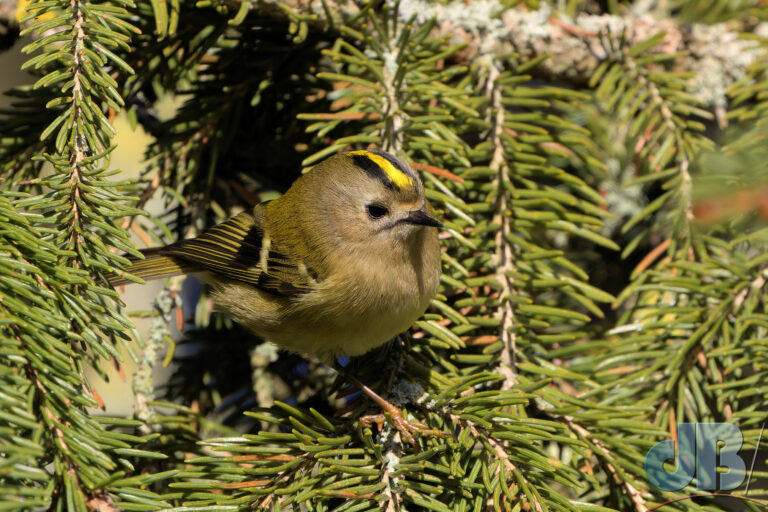
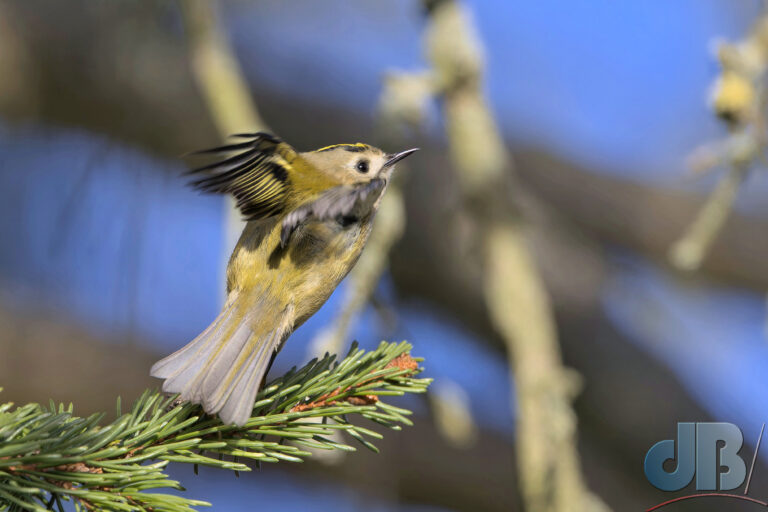
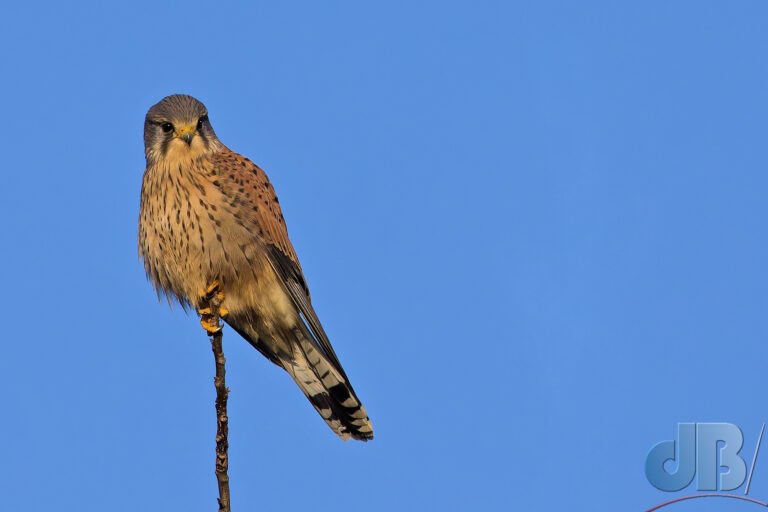
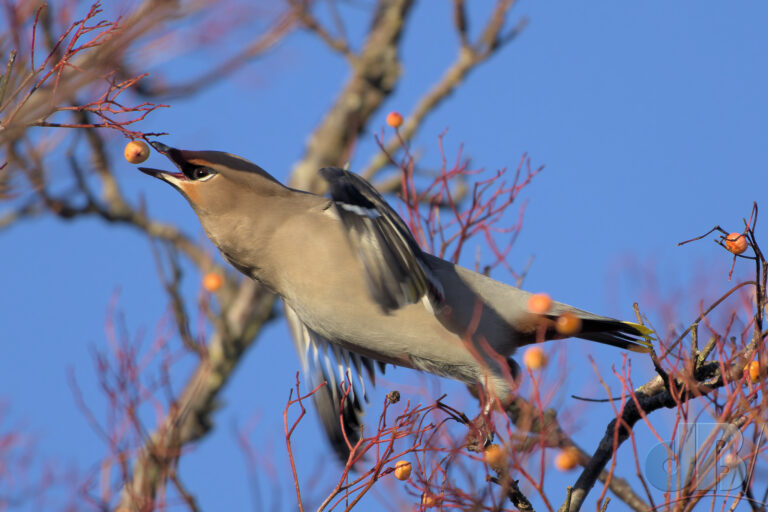
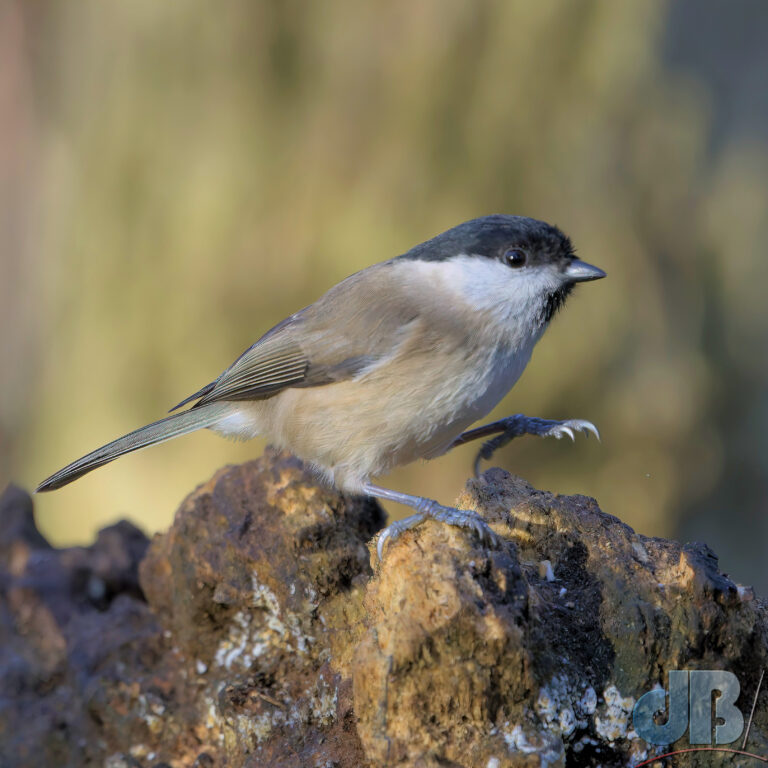
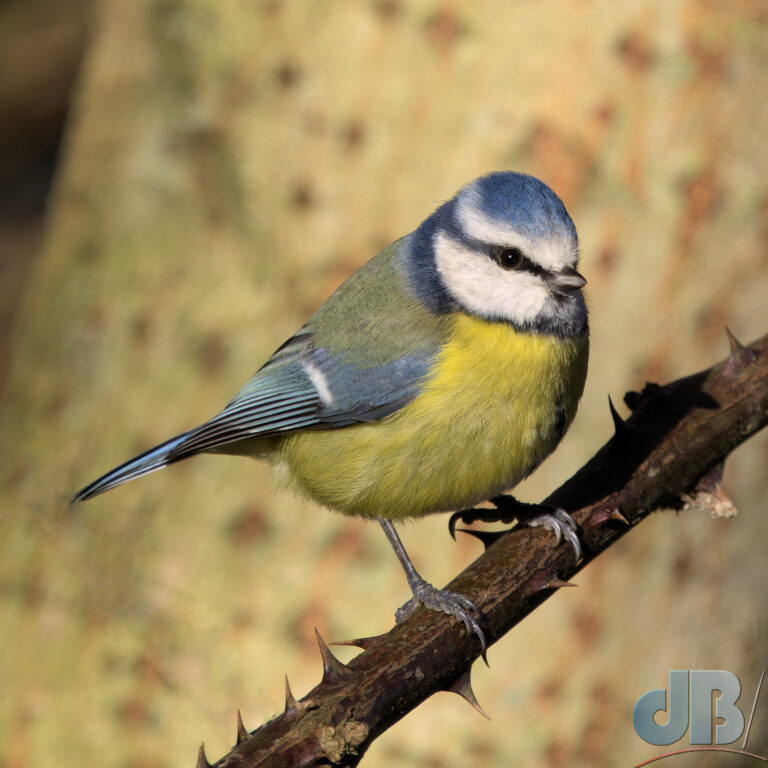
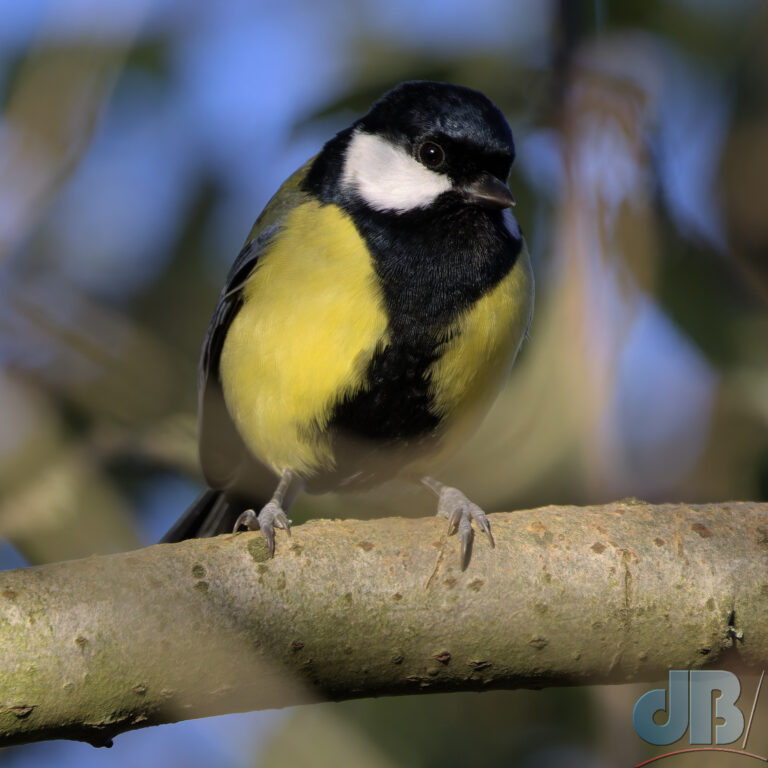
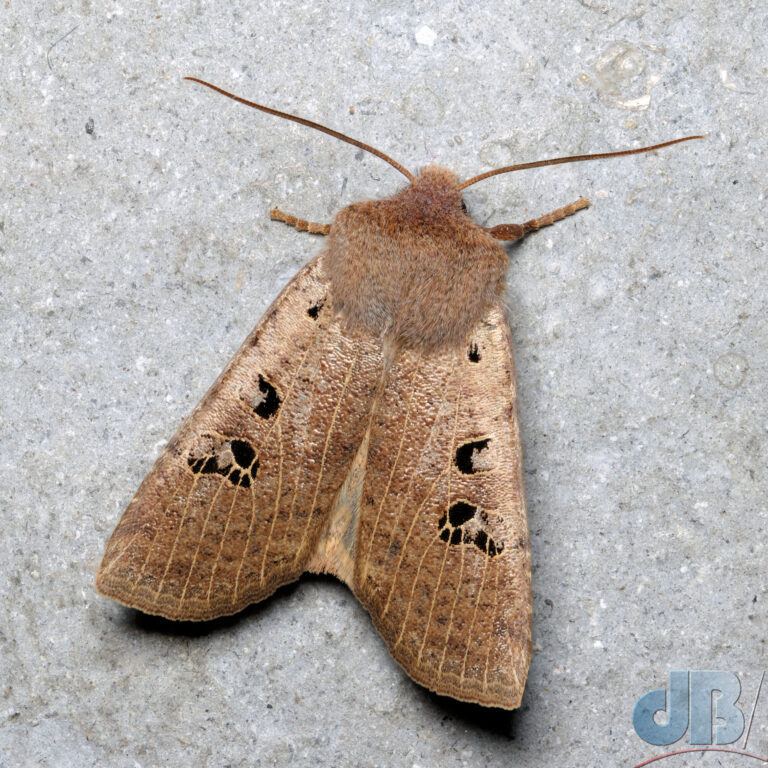
In recent years, I’ve pulled together an end of year diary entry to remind me and Mrs Sciencebase of the various natural sightings we’ve had during the year. I normally post it on New Year’s Eve, but am bringing it forward this year so that it sits as the most recent blog post as we approach Christmas. It’s just notes rather than a proper article, simply une aide mémoire.
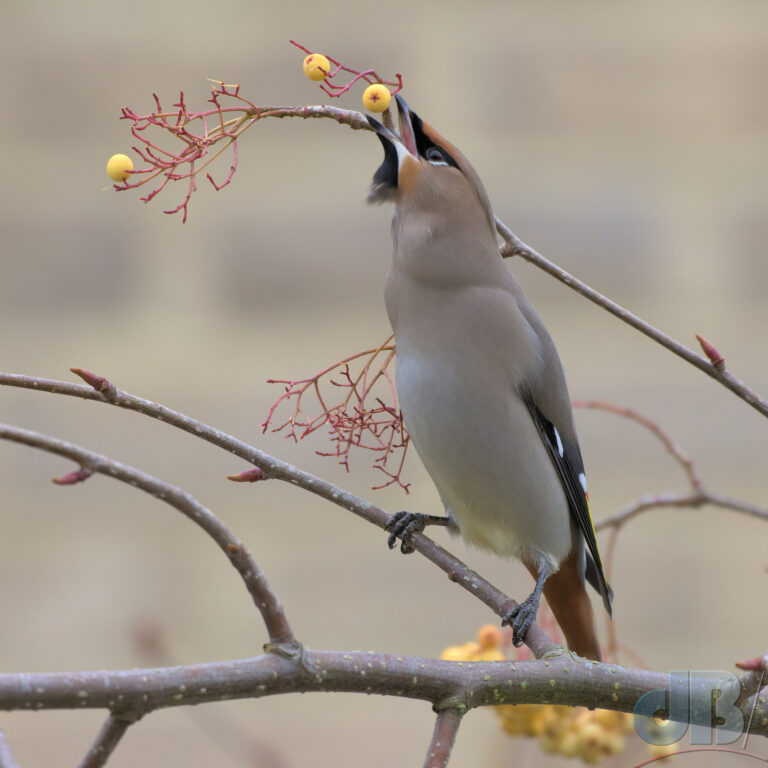
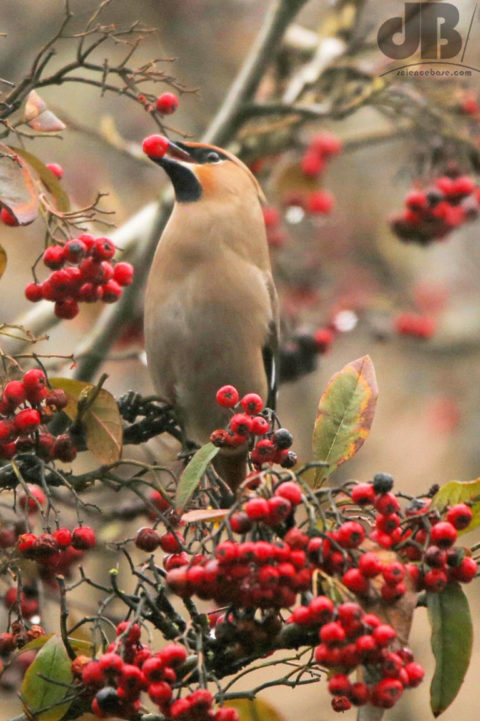
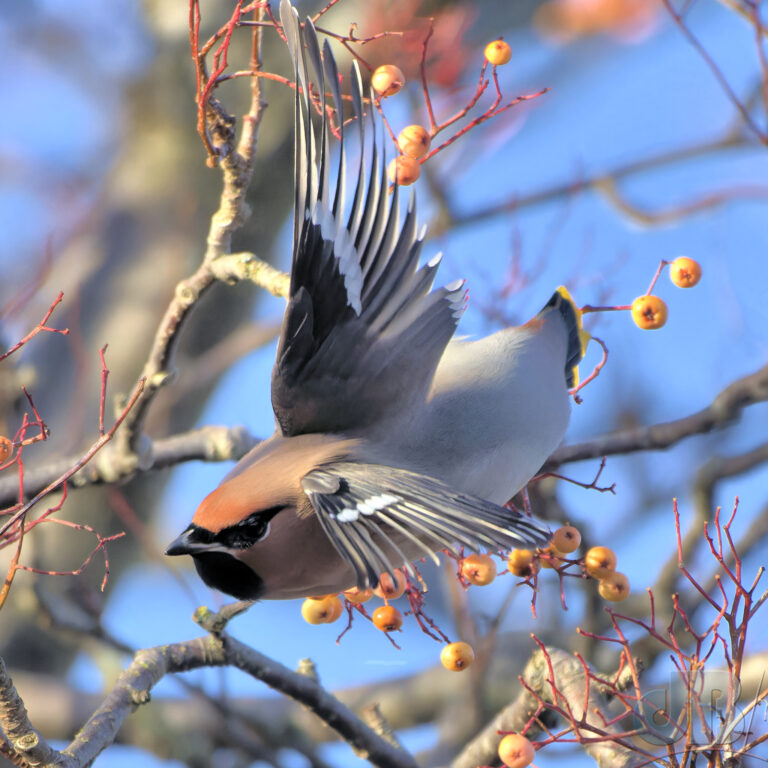
So, strangely, we spent some of New Year’s Day 2024 hanging around the railway station in Great Shelford rather than trekking the north Norfolk coast. We were there to watch the irruption of Waxwings feeding on mistletoe berries. They stayed high, but would occasionally swoop in to take the presumably much more palatable rowan berries from the shorter trees. I think we’d peaked at 34 birds at the end of December here. Too many twitchers and toggers around, the birds were showing, but nervous.
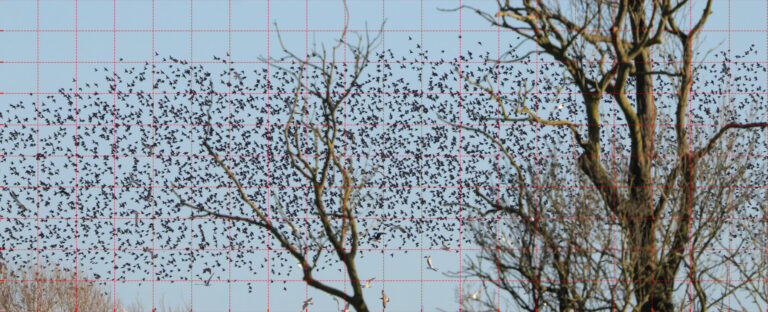
Fewer Red Kites at the landfill this winter, but still got some nice closeups in early January. Also, several thousand starlings murmurating during the day there, and active hares on the neighbouring farmland.
Great views of the Holkham (Norfolk) Shore Larks this year when we finally got to North Norfolk for a visit. Distant dogwalkers flushed the birds from their feeding patch and sent the birds in our direction. They settled about 50 metres away. Also saw Ruff and Pink-footed Geese on that trip. We stayed at Briarfields hotel next to RSPB Titchwell. Red Kites over the fields behind during breakfast.
A White Stork turned up on farmland in Cottenham having spent more time a little further out, mid-February.
Once again, we are with spawn by 22nd February in the garden pond. Tadpoles a few weeks later.
Watched enormous Starling murmurations at RSPB Ouse Fen (Earith). First visit, perhaps half a million birds murmurating at between half a mile and a mile away. Four Short-eared Owls beforehand. Also, a pair of Cranes in to roost just before the Starlings went to bed. Next visit, just a couple of hundred thousand, but they were very close and overhead at various times. The Starlings settled to roost in the reedbeds close to the car park. Next visit with Mrs Sciencebase, Short-eared Owls again and Chinese Water Deer. Visit after that very few Starlings, a thousand or so, but several Bittern calling a sight of one on a hop from spot to spot in the reeds.
Three Russian White-fronted Geese at RSPB Berry Fen hanging out with some Greylags. Nice close views, early March.
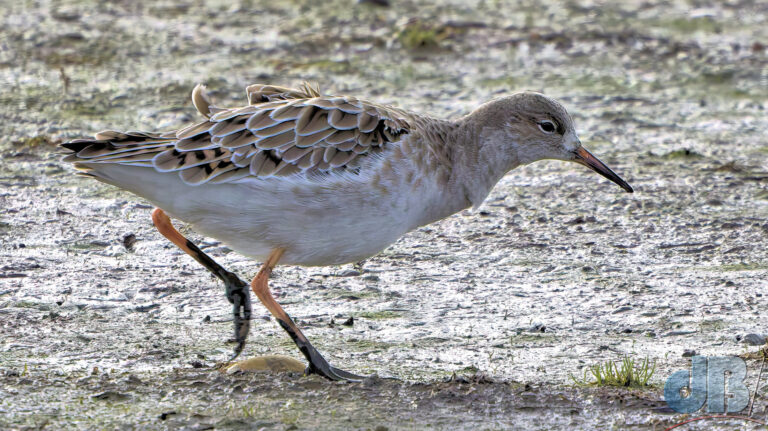
Big flock of Black-tailed Godwit in the distance not far from Swavesey Lake, also Pintail there and Great White Egret (as ever), mid-March. There were also at least 13 Cattle Egrets in one of the fen drains not far from the guided busway dropoff.
17th March, spotted a male Orange Tip butterfly. First of the year for me and first recorded nationally in 2024. It was a week earlier than Orange tip in our region according to first appearance records going back to 2007.
20th March – my first Small Tortoiseshell of the year on a walk near Swavesey Lake with Andy H. Also 34 Cattle Egrets. Largest flock of that species I’ve seen.
17th April – Spotted a Sandwich Tern fishing at Brownshill Staunch. I alerted the Over Birders’ WhatsApp group, all very excited, it ended up at Ferry Lagoon, Fen Drayton. Stayed for several days.
14th May – Northern Lights at Henley-on-Thames while camping, basically white stripes in the night sky, if only we’d known, we’d have done some long exposure, night, shots with phones and seen the colours.
24th May – Failed miserably to see the Red-footed Falcon at RSPB Fen Drayton, but there were numerous Hobby. Did see the Great Reed Warbler at RSPB Ouse Fen (Earith).
June – Butterflying and birding trip to Greece
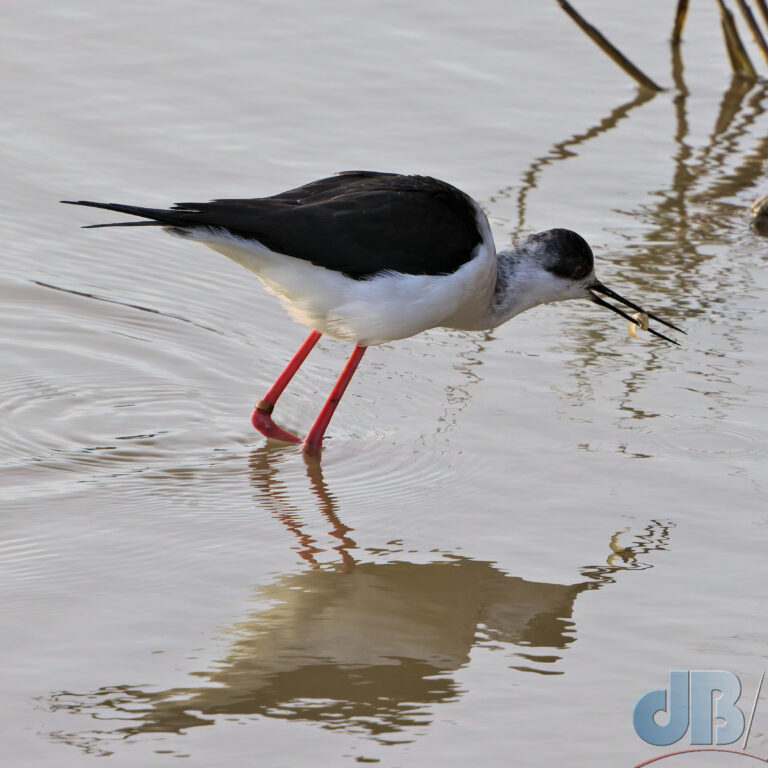
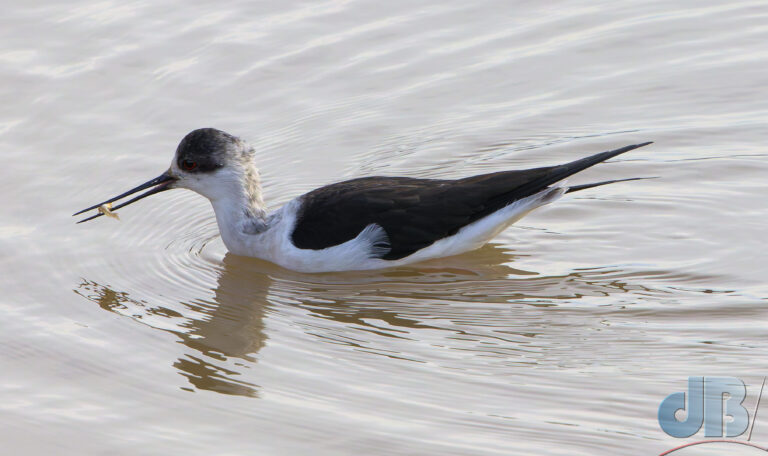
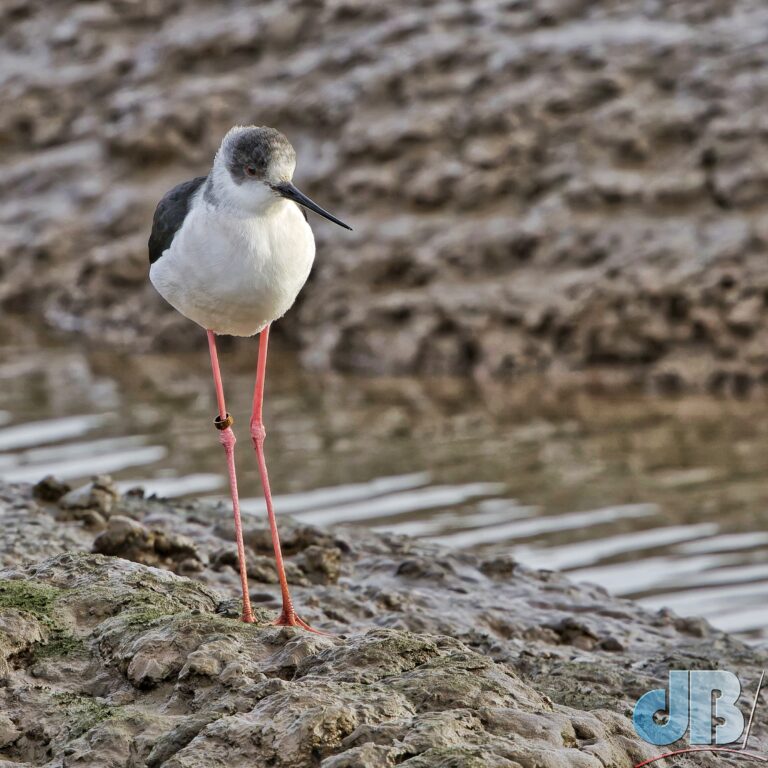
July – Pair of Black-winged Stilt on Smithy Fen.
August – Lovely week in Blakeney on the north Norfolk coast, seals, birds (Spoonbills, Sandwich Terns, Wood Sandpiper, Green Sandpiper etc, moths
Early September – moth numbers up, Convolvulus Hawk-moth again, but also some lovely new species including Palpita vitrealis and Clouded Magpie. Also female Tawny Owls calling from somewhere on Pelham Way rather than the gardens behind us.
15 September – Osprey (juvenile female and briefly an adult) at Milton Country Park. Apparently, still present as of 7 October.
September – Red and Fallow Deer at Bradgate Park, en route to Tidza.
October – We didn’t try to see the Lisbon/Tegus flamingos in the end. We did tick a few bird species in Belém and in the Lisbon Botanic Gardens etc including Crested Myna, Black Redstart, Blue-crowned and Rose-ringed Parakeets, Short-toed Treecreeper etc. Meanwhile, Yellow-browed Warblers in Milton while we were in Lisbon.
11th October – Northern Lights over Cottenham, after choir. Mostly a diffuse red glow but nevertheless filling much of the sky.
15th October – Tallying moths, 40 per session compared with 80+ in 2019. 334 species though, so diversity roughly the same year on year.
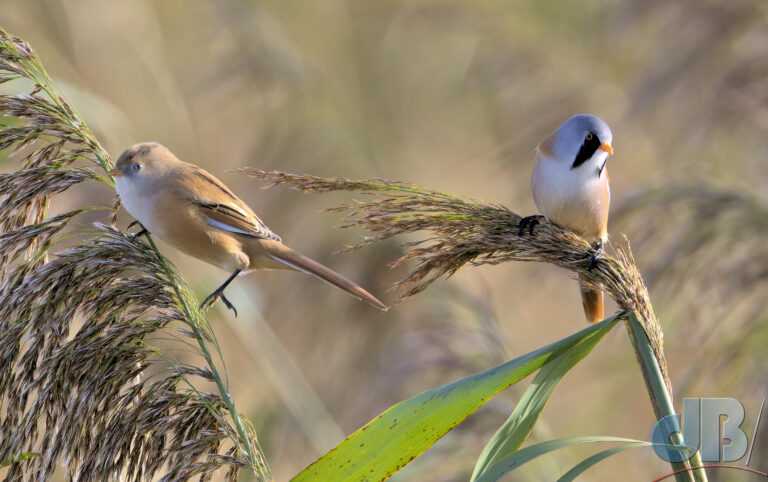
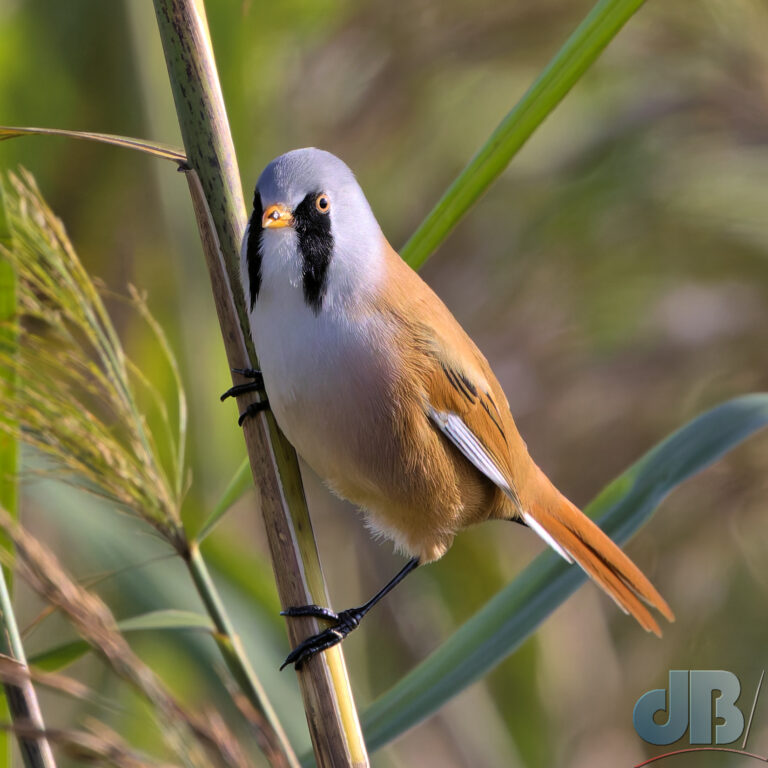
October – 17th. Bittern, Great White Egrets, beardies, and then…juvenile Purple Heron at RSPB Earith.
October – 20th and 21st – last chance in 2024 for Snettisham Wader Spectaculars…will we get there?
November – 10th. My first Black-spotted Chestnut, outside the trap. Nice species, a little like an SHC but with the markings “broken” up.
November – 13th. Starling Murmurations (several thousand birds) and one Short-eared Owl so far at Ouse Fen, Earith
November – 15th. Definitely not a natural highlight, but we said goodbye to my Dad today and gave him a tremendous send-off.
December – I dipped out on the Penduline Tit that was spotted at RSPB Ouse Fen, Earith.
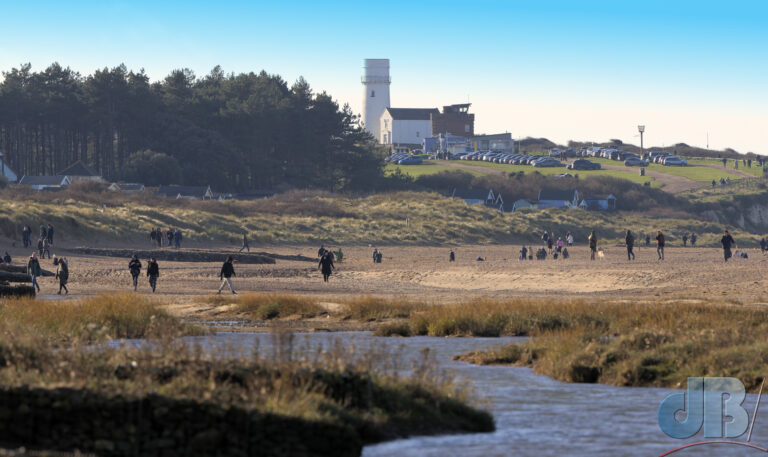
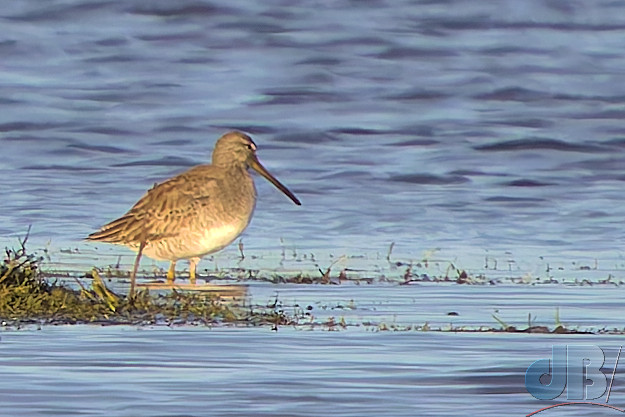
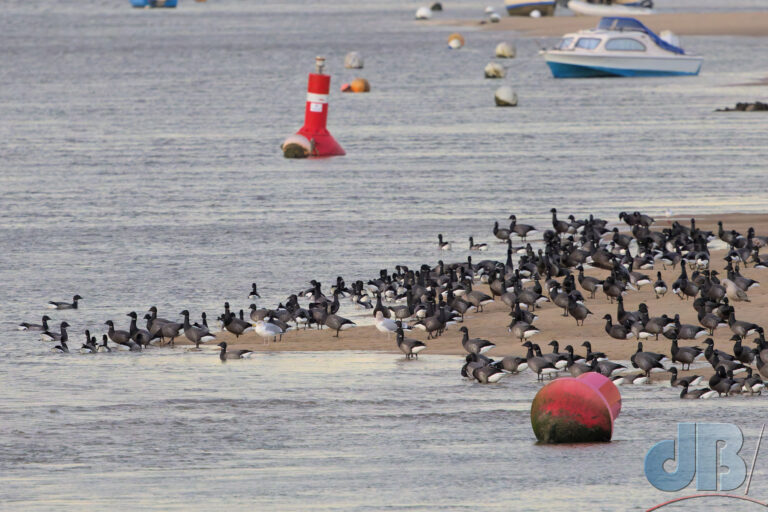
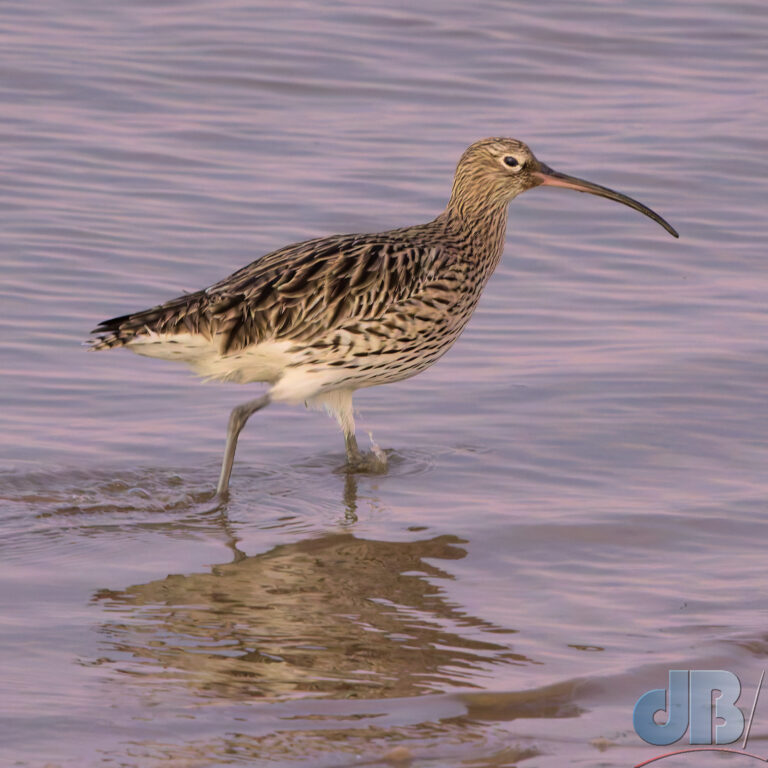
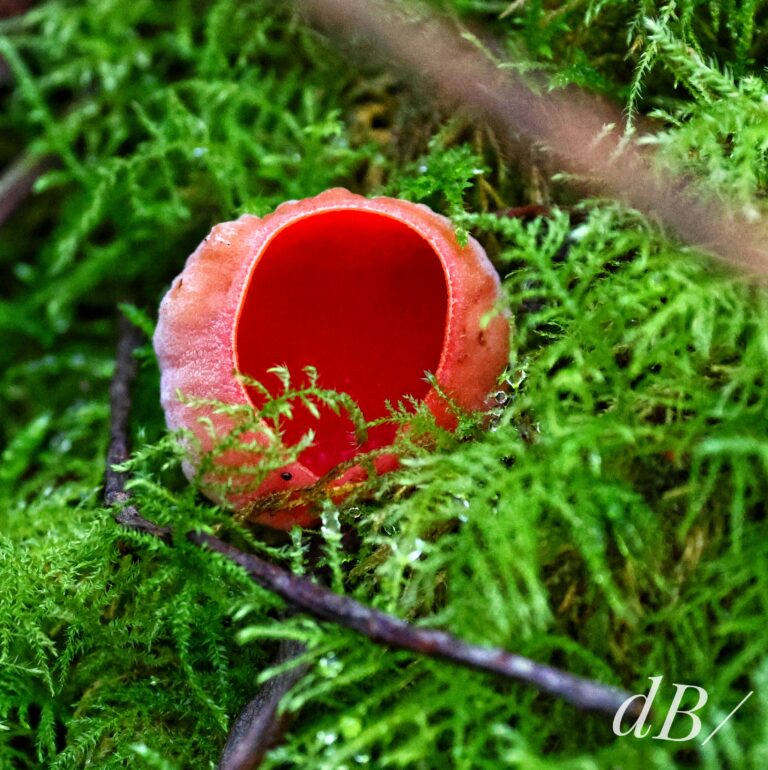
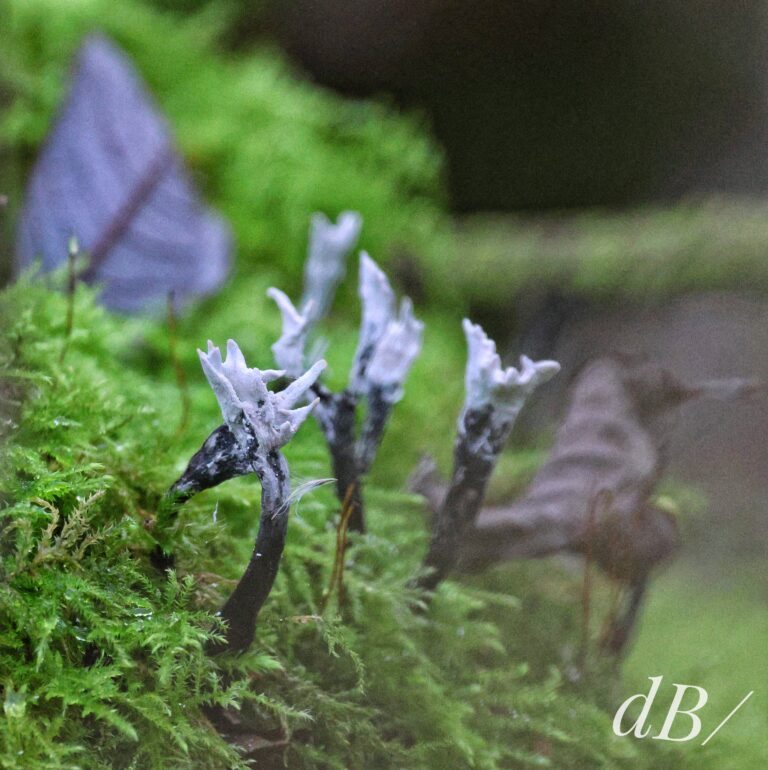
December – 30th to New Year’s Day – North Norfolk (Hunstanton, Holkham, Wells, Titchwell) – No Glaucous Gull, no Shorelark, but Long-billed Dowitcher at Holkham, lots of Brent Geese at Wells, Black-winged Stilt, Tawny Owl, Scarlet Elfcup, Candlesnuff at Titchwell. More about our end of year trip to the North Norfolk coast in a separate article.