Last night was a very different night of mothing. It had been up to 20 degrees Celsius during the day but got down as low as 7 degrees Celsius in the night, it was still and dry, with a waxing gibbous moon. The haul one gets to an actinic light moth trap can never be predicted, but numbers were the highest they had been since the warm patch in April 2019, it’s now mid-May 2019.

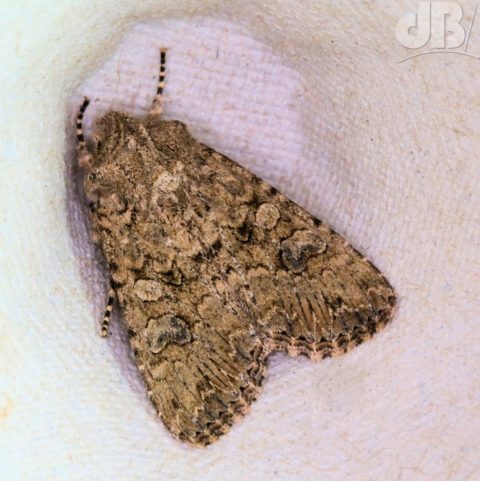
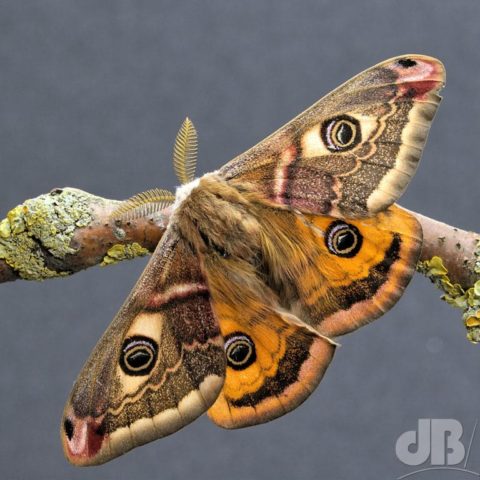
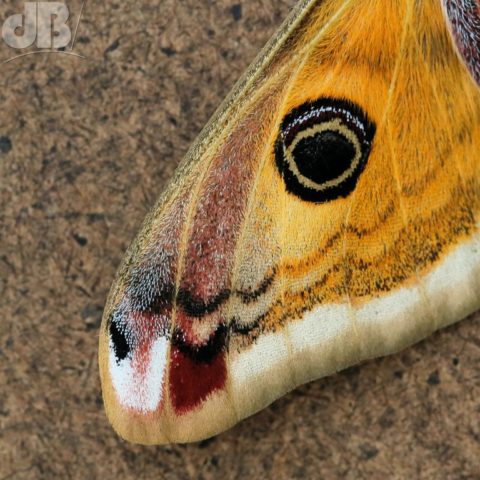
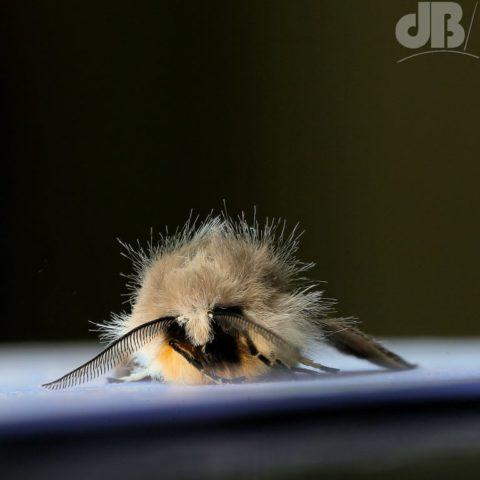
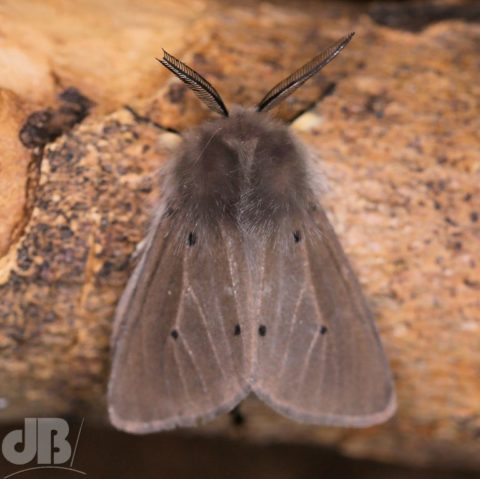
I was very pleased to see one of the larger British moths sitting on the outside of the trap this morning, the very furry Puss Moth, Cerura vinula. This specimen was an impressive 4.5 centimetres long from front leg to wingtip and has the most striking patterning.
As you can see from my photos it is very furry, has broad white wings. The forewings have very dark concentric lines that look like indentations, there are dark cross veins on the wings and bronze lines radiating down the thorax. This specimen also has a greenish hue to its heads and black spots. Gently coaxing it from the trap into an examination pot was quite an eerie feeling, the large size and furriness make you think you’re handling a small, alien-looking mammal, rather than an insect.

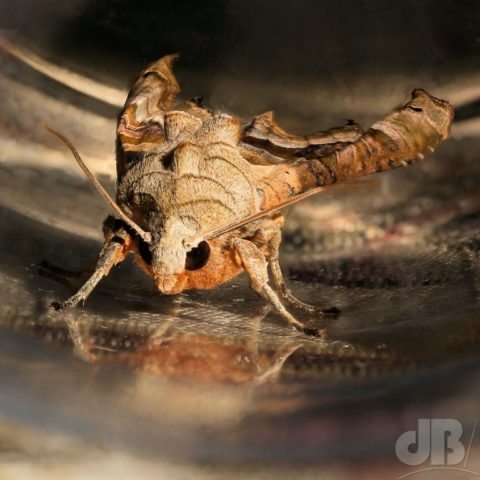
Also new for me, potted as it approached the trap last night was a Coxcomb Prominent, Ptilodon capucina, a species common from Ireland to Japan in the Palearctic ecological zone.

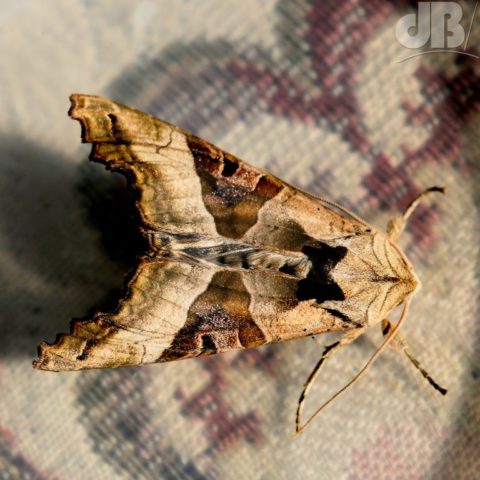
It was the busiest night for moths in the garden last night for a month or so, also ticked this morning and last night, 12 species, 20 specimens:
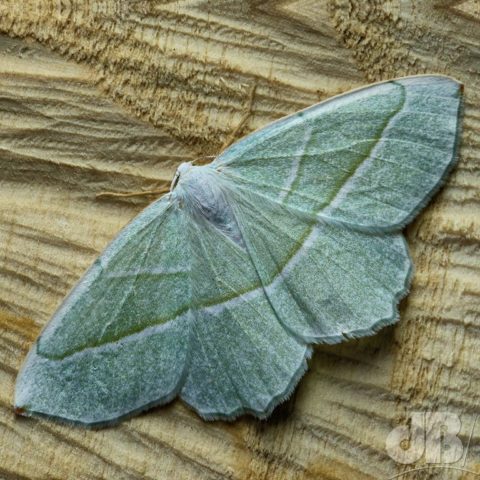
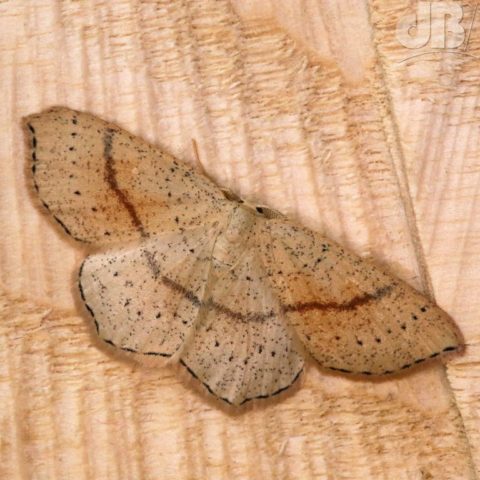
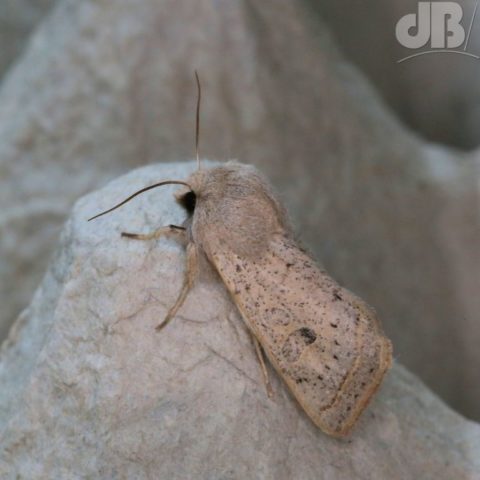
Puss Moth, Red Twin-spot Carpet, Hebrew Character, male Muslin (2x), Shuttle-shaped Dart (6x), Turnip Moth (2x), The Streamer, Double-striped Pug, Common Pug, Heart & Dart (2x), Light-brown Apple Moth.
Incidentally, I remember seeing photos of the Puss Moth caterpillar in books when I was a child, it was often the cover star of a wildlife book, for instance. You may recognise it too. Incidentally, don’t annoy this larva, it can spray formic acid at you…